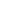
Types of Capnographs
| Main-stream capnographs | Side-stream capnographs |
 |
 |
| CO2 sensor located between endotracheal tube and breathing circuit | Sensor is located in the main unit and CO2 is aspirated via a sampling tube connected to a T-piece adapter located between endotracheal tube and breathing circuit. |
| Side-stream Capnographs |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
Easy to connect No problems with sterilization Can be used in awake patients Easy to use when patient is in unusual positions such as in prone position Can be used in collaboration with simultaneous oxygen administration via a nasal prong |
Delay in recording due to movement of gases from the ET to the unit Sampling tube obstruction Water vapor pressure changes affect CO2 concentrations Pressure drop along the sampling tube affects CO2 measurements Deformity of capnograms in children due to dispersion of gases in sampling tubes |
| Main-stream Capnographs |
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
No sampling tube No obstruction No affect due to pressure drop No affect due to changes in water vapor pressure No pollution No deformity of capnograms due to non dispersion of gases No delay in recording Suitable for neonates and children |
Contrary to the earlier versions, the newer sensors are light weight minimizing traction on the endotracheal tube. (see below) Long electrical cord, but it is lightweight. Facial burns have been reported with earlier versions. This has been eliminated with newer sensors (see below) Sensor windows may clog with secretions. However, they can be replaced easily as they are disposable. Difficult to use in unusual patient positioning such as in prone positions. The newer versions use disposable sensor windows thereby eliminating sterilization problem (see below) |